In complex systems, pumps can be connected in series or in parallel. In series operation the heads are added together and in parallel operation, the flow rates of the pumps are added. Series and parallel configuration of pumps behave similar to series and parallel configuration of electric resistances in electric circuits. The pump correlates with the electric resistance, the flow correlates with the electric current and the head with the voltage.
With pumps are studied individually, in series and in parallel configuration.
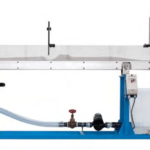
The experimental unit contains two identical centrifugal pumps and an intake tank with overflow. The overflow ensures a constant suction head in the tank, regardless of the water supply. Ball valves in the pipes allow easy switching between series and parallel operation.
Pressures at inlet and outlet of the two pumps are displayed on manometers.
Learning Objectives And Experiments
- Investigation of pumps in series and parallel configuration
- Determining the head
- Recording the pump characteristics
- Determining the hydraulic power
- Determining the operating point
Features
- Series and parallel configuration of pumps
- Determining pump characteristic curves
Specification
- Investigation of series and parallel configuration of pumps
- Two identical centrifugal pumps
- Transparent tank as intake tank
- Overflow in the tank ensures constant suction head
- Ball valves used to switch between series and parallel operation
- Manometers at inlet and outlet of each pump
- Flow rate determined by base module
- Water supply laboratory supply
Technical Specification
- 2x centrifugal pump
- Power consumption: 370W
- Max. Flow rate: 21L/min
- Max. Head: 12m
- Tank: 13L
- Pipes and pipe connections: PVC
- Measuring ranges
- Pressure (inlet): 2x -1…1,5bar
- Pressure (outlet): 3x 0…2,5bar
- 230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
- 230V, 60Hz, 1 phase; 120V, 60Hz, 1 phase