In practice, several pumps are often installed either in parallel or in series configuration for economic reasons. In in parallel configuration the pumps operate in a common pipe. This requires that the pumps used in each case can achieve the same head. Parallel configurations offer the advantage that when demand is low only one pump works and other pumps are switched on as the flow rate increases. In series configuration pumps with equal flow rates are arranged in a row. This arrangement allows the bridging of large heads and is often more cost-effective than the use of a single pump with large head.
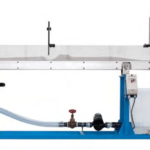
The trainer studies the cooperation of two centrifugal pumps and illustrates the differences in parallel and series configuration. The metrology components used are common in industry and therefore closely related to practice.
Learning Objectives And Experiments
- Investigate behaviour of centrifugal pumps in operation
- Recording pump characteristics
- Recording system characteristics
- Determining efficiency
- Investigation of series and parallel configuration of pumps
- Starting up and shutting down pump systems
Features
- Operation of centrifugal pumps in parallel and series configuration
- Identification of pump and system characteristics
Specification
- Trainer with 2 centrifugal pumps which are operated in series or parallel configuration
- Closed water circuit
- Drive motors with adjustable speed
- Motor with pendulum bearing, torque measurement via lever arm and force sensor
- Inductive speed sensor on the motor
- Electromagnetic flow meter
- Digital displays for power consumption, torque, speed, pressure and flow rate
Technical Specification
- 2 pumps
- Max. Flow rate: 18,5m3/h
- Max. Head: 19,6m
- 2 drive motors
- Power output: 1,1kw
- Speed range: 0…3000min-1
- Supply tank: 96L
- Measuring ranges
- Pressure (inlet):
- Pump 1: -1…0,6bar
- Pump 2: -1…3bar
- Pressure (outlet):
- Pump 1: 0…2,5bar
- Pump 2: 0…6bar
- Flow rate: 0…480L/min
- Speed: 2x 0…3000min-1
- Torque: 2x 0…10Nm
- Power: 2x 0…2,2kw
- 230V, 50Hz, 1 phase
- 230V, 60Hz, 1 phase; 230V, 60Hz, 3 phases