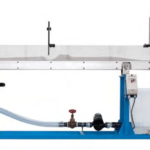
The device is designed to show the relationship between the drag coefficients of falling spheres and their Reynolds’ number value. The spheres fall through a number of different liquids contained in 2 vertical glass tubes. As the spheres have a projected area of only 1% max of the tube cross-section, wall effect is reduced to a minimum. Timing the passage of the particle between two marks on the walls of the glass tubes allows measuring their rate of fall. Different particles covering a range of sizes and densities are supplied.
TRAINING PROGRAM:
• Measurement of drag coefficients of spheres as a function of their Reynolds’ number
• Effect of particle shape on rate of fall and on drag coefficient
• Effects of boundary layer separation on motion of spheres
TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS:
• Wall mounted compact apparatus
• Two transparent vertical glass tubes, height 1500 mm, internal diameter 92 mm, complete with calibration marks
for timing
• Fluorescent lamp on the backside to make easier the visualization of the phenomenon
• Device to insert easily the particles at the top of the tube
• Device to remove easily the particles from the bottom of the tubes
• Spheres of different sizes and materials
• Two streamlined shapes
• Stopwatch
• Glass beaker
• Power supply: 230 Vac 50 Hz single-phase – 0.2 kVA (Other voltage and frequency on request